一句话或一幅图解释原理。
overriding vs overloading

图片[来源][override-vs-overload]。
依赖注入(DI, Dependency Injection)
1 | // 非依赖注入 |
在Java中,什么时候可以省略数组的大小?
一句话:声明的时候可以忽略,但是创建的时候不能省略,因为数组的大小是不可变的。
1 | int[] a; // ok, declare. |
不论是多少维的数组,创建时第一个维度信息都不能省略,其他维度信息则可以省略,为什么?
答:
一个N维数组其实可以就是:一个一维数组,其元素为N-1维的数组。所以创建N维数组的时候,
第一个维度信息不能省略,但是试图访问具体元素时就会出现空指针,因为并未开辟内存空间。
如何获取数组和字符串的长度信息?为什么?
1 | int[] arr = new int[3]; |
因为数组对象有一个length属性,而且是不可变的,而字符串使用字符数组保存数据,
字符数组本身就有长度信息,所以String没有length属性,故提供length()方法。
Java中,equals()和hashCode()的关系
两个对象,
- 如果equals()为true,则hashCode()返回值一定相等
- 如果hashCode()返回值相等,equals()不一定为true
在HashMap中,查找对象时,首先根据其hash code进行快速定位,如果找到了,在根据equals()值判断是否相等,如果相等则找到了,否则就返回Null。
所以,
- 如果两个对象equal,但是hash code不相等,则要么第一步就找不到,要么第二步
equals()为false,总之就是找不到该对象。 - 如果两个对象hash code相等但是equals()为true,则会把不同对象hash到同一个“槽”里面,
但是这种情况是运行的。
Java中的各种initializer
1 | public class Foo { |
输出,
1 | static initializer called |
instance initializer不常用,比较可以在构造函数里面做这些事情就好了,
但是有一种情况:匿名内部类,可以使用instance initializer,并将它没有自定义的
构造函数。
1 | HashMap<String, String> m = new HashMap<String, String>() { |
Java exceptions
一句话:
- cheched exception表示program之外发生的异常,program对此无能为力,需要programmer介入处理,如file not found;
- unchecked exception表示program本身发生的异常,是program自身的逻辑问题,如除数为0。
Exception hirachy:
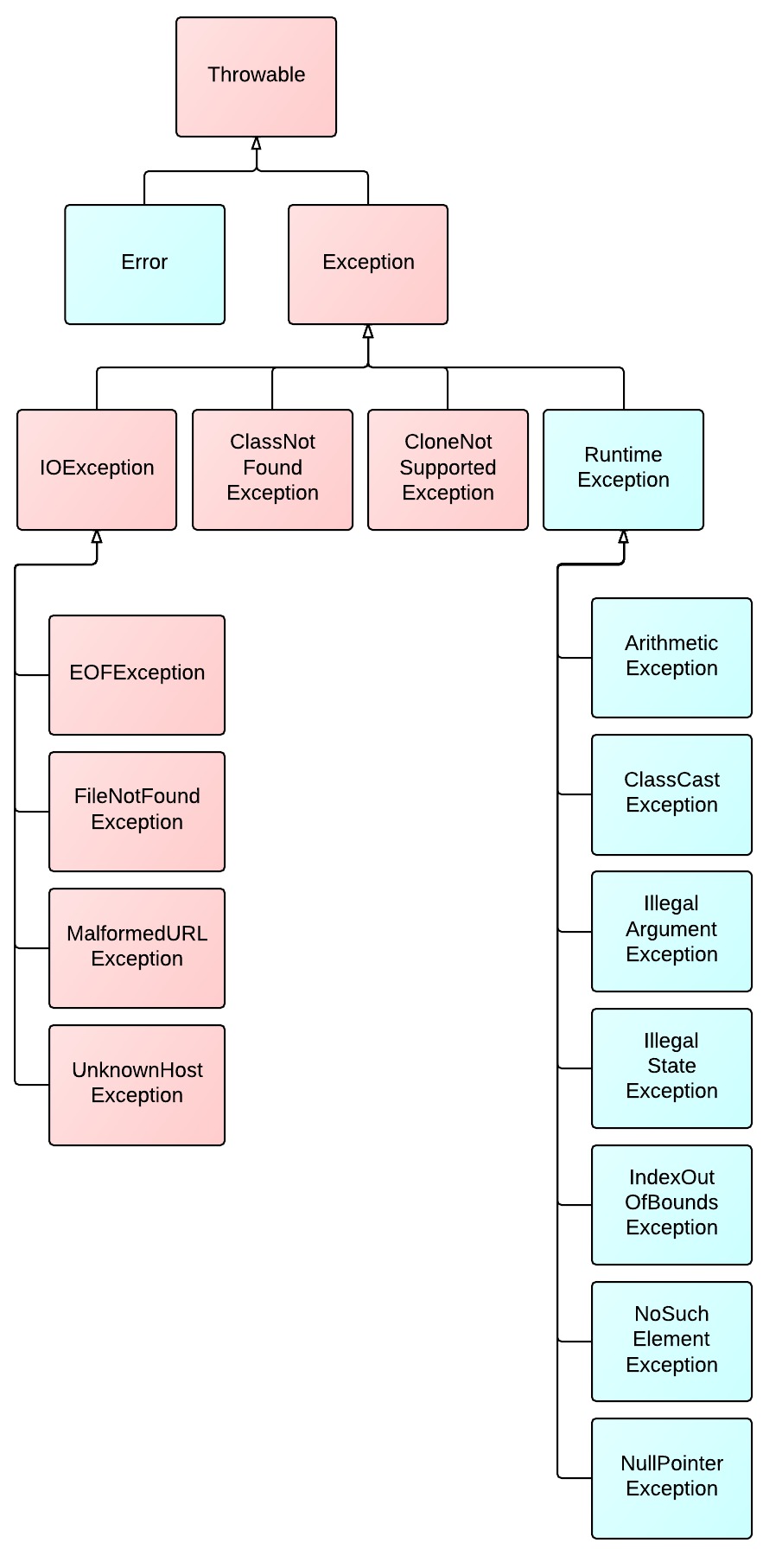
红色表示checked exception,蓝色表示unchecked exception。
compiler会关注checked exception,这类exception必须处理,否则编译不过。
所有Exception均可以捕获,
1 | int a = 0; |
代码[来源][dependency-injection]。